Table Of Contents:
- What Are The Dimensions Of A Basketball Court?
- Standard Court Sizes Across Levels
- Half Court Vs Full-size Court Dimensions
- Basketball Court Line Marking Standards
- The History of Basketball Court Dimensions
- FAQs On Basketball Court Dimensions
- Build Your Basketball Court With PROformance
Key Takeaways:
- Basketball court dimensions vary by level of play, with NBA and NCAA courts measuring 94′ × 50′, high school courts at 84′ × 50′, and FIBA courts using metric dimensions, making it essential to match your court size to its intended use.
- Measurements like rim height, free-throw distance, three-point lines, and key width are standardized, but differ slightly across leagues, directly impacting gameplay, spacing, and player development.
- Full courts, half courts, and standard courts can all be effective when designed correctly, as long as proper line markings, safety clearances, and surface considerations are followed to ensure performance and long-term durability.
Understanding the official court size is the first step in creating a basketball court that plays well, remains durable, and is safe for each level of gameplay you intend to accommodate. Whether you are designing an indoor facility, an outdoor park facility, or a home facility, it is crucial to use the correct dimensions to maximize safe spacing, playability, and performance.
In this blog, we provide a comprehensive breakdown of the official court dimensions for high school, college, and professional basketball (NBA, NCAA, FIBA). Additionally, we will also discuss the measurement of a few other key elements, such as the free-throw line, the three-point arc, the key/paint area, and the height at which the basketball should be rimmed. Understanding these areas will help you to make informed choices on your court installation and/or design and performance equipment.
What Are The Dimensions Of A Basketball Court?
Court Dimensions by Level –
- NBA / NCAA: 94 ft × 50 ft
- High School: 84 ft × 50 ft
- FIBA: 28 m × 15 m (approx. 91.9 ft × 49.2 ft)
Other Basketball Court Measurements –
- Rim Height: 10 feet from the playing surface (all levels)
Free-Throw Line:
- NBA/NCAA: 15 feet from the backboard
- FIBA: 4.6 meters (15.09 feet) from the backboard
Three-Point Line:
- NBA: 23’9” at the top, 22’ in the corners
- NCAA: 22’1.75”
- High School: 19’9”
- FIBA: 6.75 meters (22.15 feet)
The Key/Paint Width:
- NBA: 16 feet
- NCAA/High School: 12 feet
- FIBA: 4.9 meters (16.08 feet)
Standard Court Sizes Across Levels
NBA Basketball Court Dimensions
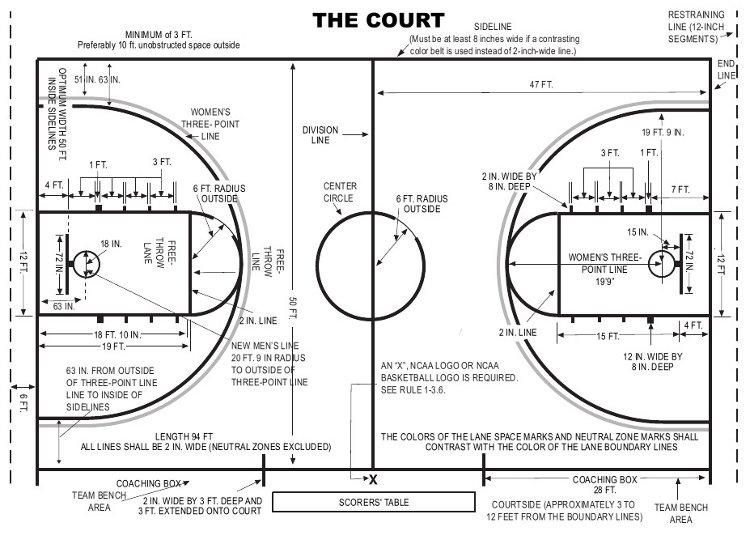
The National Basketball Association (NBA) court size is 94 feet long and 50 feet wide, and the half-court line divides the court into two equal sections. A circle with a radius of 6 feet is often located at the center of the court with the logo of the home team in it.

The “key” (also known as “the paint”) is 16 feet wide and 19 feet from the baseline to the free-throw line. There is a semicircle with a radius of 6 feet at the free-throw line, and many basketball courts show the other half of the semicircle as a dashed line so players can clearly see where to jump for a jump ball.
A 4-foot backboard is located 4 feet from the baseline, and the rim is always 10 feet in height. This makes the distance from the backboard to the free-throw line 15 feet, as well as the distance from the foul line to the center of the court 15 feet. The backboard is 6 feet wide and 42 inches high. The restricted area is marked by a 4-foot semi-circular arc that extends around the foul line area to mark where defenders are not allowed to take a charging foul. The free-throw lane spaces are marked off by a distance of 3 feet, beginning with the first space at 7 feet from the baseline.
Beyond the paint, the NBA three-point line uses a combination of straight lines and an arc:
- 22 feet from the basket at the corners
- 23 feet, 9 inches at the top of the arc
This design provides a way to keep the arc from going beyond the boundary.
The sidelines should have a line on them that measures 28 feet in length in each direction from the center of the court, which forms the team bench area and designates where the ball should be placed after timeouts and specific fouls.
WNBA Basketball Court Dimensions
The Women’s National Basketball Association (WNBA) courts are the same size as NBA courts, which are 94 feet long by 50 feet wide. WNBA courts also have identical rim heights, free throw distances, and backboards to those of NBA courts (i.e., 10-foot-high hoops, 15-foot free throw lines from the backboards, and 6-foot-wide by 42-inch-deep backboards). The only difference between WNBA and NBA courts is the location of the three-point line, which is located at 22 feet (approx.) from the basket in the WNBA with a uniform arc (i.e., a round arc).
All other markings (i.e., keys, restricted arcs, and lane spaces) are located on WNBA courts using the same locations as those of NBA courts.
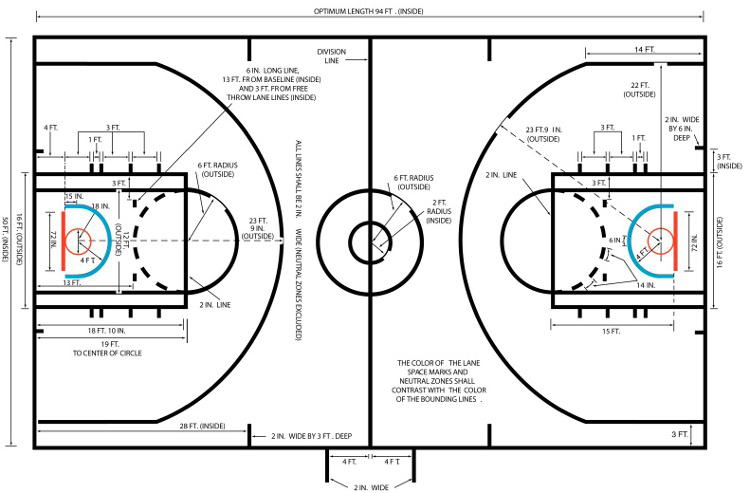
NCAA Basketball Court Dimensions
The National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA) basketball courts have similarities to those of the NBA and WNBA, such as court dimensions, foul line distance, height of basketball hoop, size and length of backboards, and the tip-off circle. However, the key (paint) is 12 feet wide in the NCAA as opposed to 16 feet wide in the NBA. Additionally, the NCAA has its first (1st) block (in the lane) located 6 feet from the baseline, while the NBA has its first (1st) block (in the lane) located 7 ft from the baseline; and, the restricted area (underneath the basket) is 3 ft in diameter for the NCAA and 4 ft in diameter for the NBA.
The most notable difference between the NCAA and the NBA is in the length of the three-point line. The length of the NCAA three-point line is 20 ft 9 in from the center of the basket, resulting in a smooth and continuous arc from the three-point line back to the hoop. Since the NCAA three-point line is shorter than the NBA three-point line, it can be one of the more difficult transitions for college players who are transitioning into professional basketball players.
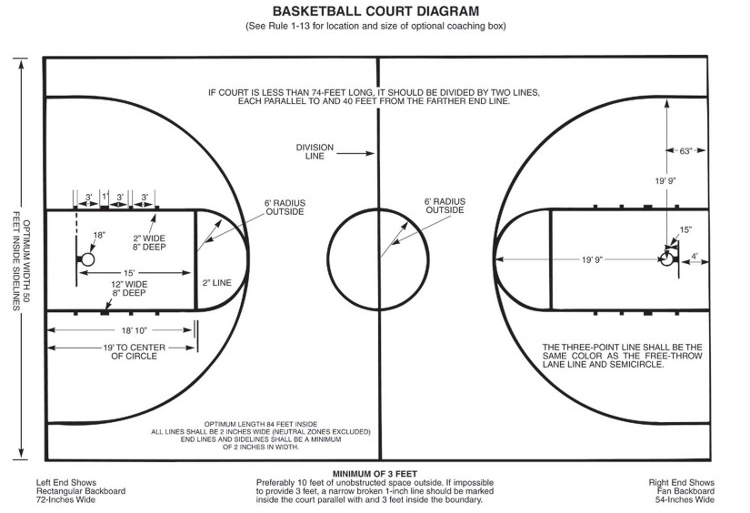
High School Basketball Court Dimensions
High school basketball courts are a little different from their college and professional counterparts. The most noticeable difference is that the court is a full 10 feet shorter, measuring only 84 feet. However, there are some similarities. The court is still 50 feet wide. The basket is also 10 feet off the ground.

The tip-off circle has a six-foot radius, just like the big kid courts, and while the high school landscape isn’t as standardized as college and professional basketball, the backboard is supposed to have the same measurements as the NCAA and NBA.
Just as in college and professional basketball, the foul line is 15 feet from the backboard, and the key is 19 feet long. It’s also the same 12 feet wide as the NCAA — four feet narrower than the NBA and WNBA.
The other visible difference is the distance from the three-point line. Shorter than either the NCAA or NBA, the high school free-throw line is just 19 feet, nine inches from the center of the basket. Additionally, high school basketball courts do not have any restricted area under the basket, since that rule doesn’t exist in high school basketball.
FIBA Basketball Court Dimensions
International basketball is overseen by FIBA, and the dimensions of their courts differ slightly from the dimensions of a U.S. basketball court because they are based on the metric measurement system.
The size of a FIBA court is 28 m by 15 m (92 feet by 49 feet). The center circle has a diameter of 3.5 m (approximately the equivalent of a standard U.S. center circle), which is slightly smaller than that of the NBA. The key is nearly the same size as a U.S. basketball court at 5.8m × 4.8m, which is close to the dimensions of a U.S. key.
There is a 1.2-meter (approximately 4 ft.) distance between the baseline and the bottom of the hoop on the basket; therefore, the free-throw line is 4.6 meters (approximately 15 ft.) from the backboard. The restricted area arc below the rim has an approximate radius of 1.25 meters (approximately 4 ft.).
The greatest difference is in the elevation of the three-point line. The three-point line of FIBA is located at 6.75 meters (approximately 22.15 ft) away from the hoop and is more than one and a half feet closer than the three-point line of the NBA. The WNBA has also adopted the same three-point distance as that of FIBA.
Half Court Vs Full-Size Court Dimensions
The size of an NBA and NCAA court is 94 feet long by 50 feet wide. High school courts are typically 84 feet long by 50 feet wide. All full courts have two ends of the court, two three-point arcs, two free throw lanes, and all of the sideline and baseline lines.
A half-court uses just one end of a full-size court. Depending on how much room you have, the dimensions of a half-court will be different, but most half-courts are roughly:
- 47 × 50 feet for NBA/NCAA (half of 94)
- 42 × 50 feet for High School (half of 84)
- 14 meters × 15 meters for FIBA (approximately)
Key elements present in a half-court include:
- 1 Basket & backboard
- 1 Free Throw Lane (key/paint)
- 1 3-Point Line (based on selected league standards)
- Sidelines & baseline
Key Difference:
With 5-on-5 players on a full court, you can expect fast breaks, transition plays, and full-court defense. A half-court is best used for shooting practice, training small groups of players, and playing 3-on-3 or home courts.
In conclusion, a half-court is a compact version of a full-size court with all the important markings on one side, taking up less room in total length.
Basketball Court Line Marking Standards
The standards for all basketball court line markings are standardized across leagues and provide the same spacing to ensure that all basketball games are played consistently with safe distances between competitors. Though there will be minor variations in how each league marks its courts, the basic markings remain the same for all basketball leagues (NBA, NCAA, FIBA, and High School).
Baselines and Sidelines
The sidelines run the entire length of the court from one end of the court to the other, while the baselines mark the boundaries for each basket (i.e., in bounds). Whenever a player steps on or across either sideline or baseline, they will be considered out of bounds.
Center Circle and Centerline
The centerline of the basketball court runs down the center of the court and separates it into two halves. The center circle is located in the middle of the centerline and is used for the opening tip-off.
- NBA/NCAA: 6-foot radius
- FIBA: 1.8-meter (5.9-foot) radius
The Key (Paint Area)
The key, also called the paint area, extends from the baseline to the free-throw line and defines positioning during free throws.
- NBA: 16 feet wide
- NCAA & High School: 12 feet wide
- FIBA: 4.9 meters (16.08 feet)
Free-Throw Line & Free-Throw Circle
All levels have the same distance for a free-throw line, which is 15 feet from the backboard. Also, there is a semicircle that connects to the free-throw line to keep players in position for both jump-ball situations and when making free throws.
Restricted Area Arc
The restricted area arc is a curved line on the ground directly underneath the basketball hoop that is designed to stop defenders from being able to receive a charging foul if they are within this area.
Three-Point Line
The three-point line forms a curved arc with straight segments near the corners to stay in bounds. Distances vary by league:
- NBA: 23’9” at the top, 22’ in the corners
- NCAA: 22’1.75”
- High School: 19’9”
- FIBA: 6.75 meters (22.15 feet)
Free-Throw Lane Spaces
The area surrounding the key has marked spaces on each side of the key that a player can line up on when shooting a free throw. The purpose of these markings is two-fold. They are to provide an equal amount of spacing for the shooter and to provide the ability to rebound on an equal basis.
Coaching Box & Bench Area Lines
Markings for the coaching box rule from the baseline along either side of the court at 28 feet from the baseline. The coaching box markings define where coaches and team personnel can stand when play is underway and when the game is on hold, and when a play is being set up for an inbound pass.
The History of Basketball Court Dimensions
Since its invention in 1891, basketball’s court dimensions have varied. Let’s look at some of its historical changes, as well as answering that nagging question — “Why are basketball hoops 10 feet high?” — below:
The Story Behind the 10-Foot High Hoop
The height of a basketball hoop, being 10 feet, seems at first glance to be something that was purposefully thought out in terms of the physical capabilities of athletes during shooting, as well as their form. Even the tallest players in the NBA today need to jump when dunking, and a rim set 10 feet in the air is also reasonable for a player in the NBA to shoot from that distance. The truth, however, is much simpler.
When James Naismith invented the game of basketball in 1891 in Springfield, Massachusetts, he merely attached a peach basket to the railing of a gym that was 10 feet high. The measurements used in creating Naismith’s original basketball rim have remained the same from the very start of its existence and will remain unchanged for the future, even though the game itself has changed greatly since Dr. Naismith created it.

The History of the Three-Point Line
The basketball three-point arc is a defining element of the game, and its history is nuanced and complex in addition to the actual three-point shot itself.
It was first introduced by the American Basketball League in 1961, almost 70 years after the creation of basketball; the intent behind this new rule was to increase excitement in professional basketball, but shortly after its introduction, the league folded, and as a result, the three-point rule did not gain any traction.
In 1967, the ABA once again introduced the three-point line, this time successfully. Fans enjoyed the new, faster-paced, and higher-scoring style of play. However, when the NBA merged with the ABA in 1976, they did not immediately embrace the three-point line as part of their league.
During the 1979-80 NBA season, the NBA finally introduced the three-point line to its league. In 1986, the NCAA adopted the three-point line as well, and one year later, high school basketball followed suit.
Over the years, the three-point line has been moved and adjusted. The NBA, in an effort to increase scoring during the 1990s, moved the three-point line closer to the basket, but eventually the league returned the three-point line to its normal distance. The NBA has had discussions around the idea of adding a four-point shot, but for now, the three-point shot is a unique and defining aspect of the sport.
The Original Cage Matches
In the early days of professional basketball, the game was played inside an actual cage. The reasons were more about practicality than about safety. The rule for who got to inbound a ball that left the court was “whoever got to it first,” so organizers took to putting up a cage so the ball could never go out of bounds in the first place.
Those first basketball courts were about a third smaller than they are today, and the cages provided a physical boundary and an extra immovable for savvy teams. Could you imagine how much different the game of basketball would be today if those cages had stuck around?
The Alternative Key Designs
Today, basketball courts at all levels share a common design for the key — a rectangle measuring either 19 feet by 16 feet or 19 feet by 12 feet. However, this was not always the case. From the creation of FIBA in 1956 until 2010, the key was a trapezoidal design that was significantly wider at the baseline.

Another design of this feature is responsible for the name “key.” Have you ever thought about how a rectangular area under a basket got such a random name?
The reason is that the original area was much narrower, while the circle surrounding the free throw line was the same size. These two factors combined to create a shape that resembled an old-fashioned key. In 1951, the key was widened to 12 feet and later to the 16 feet we see now in the NBA and FIBA.
While the term lives on, time has erased any record of its design and original reference. And for the record, the official name for this feature is “free throw lane,” which isn’t a phrase many of us hear often.
And that’s a wrap on the history of basketball’s court dimensions.
FAQs About Basketball Court Dimensions
How Much Space Do You Need Around A Basketball Court?
Basketball courts should have a minimum of 6 to 10 feet of open space on all sides of the court in order to provide players with an adequate amount of clearance to stop before hitting a wall or fence, as well as give the referees and any other equipment that may be present.
In general, the minimum amount of clearance around basketball courts is typically 6 feet of unobstructed space, whereas the recommended amount for competitive biking and training courts would be at least 8-10 feet of unobstructed space to allow for faster action and better safety for all involved.
For indoor basketball courts, ceiling height may also be an important factor in planning clearance. Many facilities plan on ceiling heights of between 20-25 feet in order to help reduce instances of interference, as well as obstacles, during play.
By providing a proper amount of space to accommodate the players and their needs, the clearance around your basketball court will enhance safety, playability, and long-term use of a basketball court, especially for high-energy and multiple-player games.
Can Basketball Court Dimensions Be Customized?
Yes, custom sizes of basketball courts are an option for those who will play on courts that are not an official NBA, NCAA, or FIBA court. Use of custom-size courts is frequently employed when the amount of available space is limited, primarily for younger children, or when the purpose of the court is for training and practice, rather than for regulated play.
Custom basketball courts do not have to conform to the same strict regulations as traditional basketball courts established by the NBA, NCAA, FIBA, and High School. Therefore, allow the owner flexibility in size, arrangement of court markings, and options for other accessories used in the game. However, to maintain safety, the owner must still abide by the same spacing and clearance requirements.
Do Residential Basketball Courts Have To Meet Official Dimensions?
No, residential basketball courts do not need any specific dimensions set by the NBA, NCAA, or FIBA. Home basketball courts typically follow the existing dimensions of each home and how the court will be utilized.
Homeowners may choose to put in half-courts or scaled-down versions of a standard-sized court that will provide a similar look and feel of regulation play, without taking up a standard-sized court footprint. While the official dimensions may be used as a reference when creating a home basketball court, comfort or safety, and functionality are of utmost concern for residential basketball courts.
How Long Do Basketball Court Markings Last?
The markings on basketball courts outside usually last 1-3 years, while indoor markings generally last 5–7 years, depending on how often they are used, how often they are exposed to the elements (rain, temperature, etc.), what type of surface was prepared as well, and the type of paint used when applied. Proper care of high-quality coatings will help to increase the longevity of markings, whereas heavy use and exposure to the sun will necessitate more frequent touch-ups.
Build Your Basketball Court With PROformance
Perhaps you don’t have 94 feet of flat asphalt or indoor floor space. Don’t worry, because residential half court setups can be just as fun. And whether you are looking to paint your court or apply a pre-made solution, sticking to the official dimensions will take your pickup games to the next level.
Take a look at our selection of goals, nets and accessories to bring your home’s court together. You’ll have a hard time dragging your kids off the court as they spend hours posting up like Boogie, slashing like LeBron and launching it from deep like Steph.